Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for the proper functioning of the body. They are important for heart health, reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, lower triglyceride levels and have anti-inflammatory effects. They can be obtained through diet or taken as dietary supplements. Learn about the effects of essential omega-3 fatty acids and where you can find them in food.
What are omega-3 fatty acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are classified as essential polyunsaturated fatty acids (EFAs). They are not produced in the human body, so they must be taken from outside sources. They are important for the proper functioning of many organs, including the heart and brain. The most important omega-3 fatty acids include:
- docosahexaenoic acid (DHA),
- eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA),
- alpha-linolenic acid (ALA).
They can be found in many food products and also provided in the form of dietary supplements.
Properties of omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are essential for the proper functioning of the body. They perform a number of important functions:
- support heart health,
- are a key component of cell membranes,
- are essential for the proper functioning of the brain, memory and concentration,
- lowers triglyceride levels,
- have a positive effect on the condition of the skin, hair and nails,
- support the reduction of excess body weight,
- reduce the risk of blood clots and metabolic syndrome,
- stimulate the immune system,
- reduce allergy symptoms,
- have a positive effect on eyesight.
Omega-3 fatty acids also have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, neuroprotective and anti-cancer effects. They are recommended for pregnant women and children. Taking omega acids prevents premature birth and supports the development of the child in the womb.
Use of omega-3 fatty acids
Studies have shown that regular intake of omega-3 fatty acids reduces the risk of heart disease and reduces mortality due to this. Supplementation brings positive results in many diseases of civilization, especially obesity, atherosclerosis, diabetes, lipid disorders and hypercholesterolemia. It also helps treat rheumatoid arthritis, some neurological diseases, depression and cognitive difficulties.
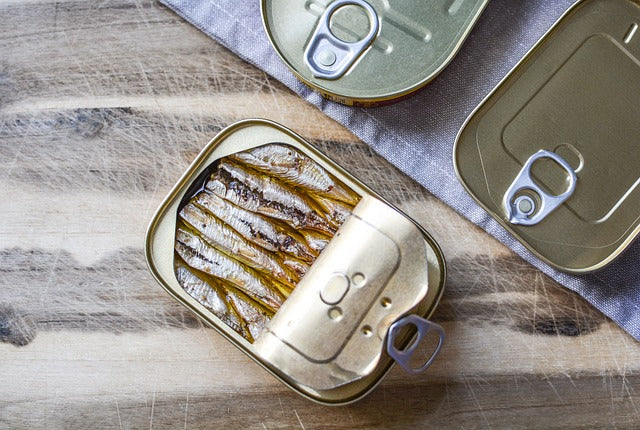
Omega-3 deficiency increases the risk of heart disease, atherosclerosis, circulatory system disease, hypertension, dementia, intestinal disease and osteoporosis. The easiest way to get EPA and DHA is through food, but not everyone has the opportunity to regularly eat oily sea fish, which are an excellent source of omega-3 acids.
Where can you find omega-3 fatty acids?
The importance of fatty acids in the diet is enormous, but their best sources are sea fish (salmon, mackerel, trout, sardines), seafood, some vegetable oils, chia seeds, flax seeds, soybeans and walnuts.
The Institute of Food and Nutrition issues nutritional standards that include recommended amounts of fatty sea fish and seafood. For adults, this is 1-2 times a week, which is not always observed, hence the need to use omega-3 acids in the form of dietary supplements.
Why is omega-3 supplementation important?
DHA and EPA deficiency can cause a number of symptoms, including weaker immunity, mood disorders, and muscle tension. It can also be seen in the skin, hair, and nails. The skin becomes dry and less elastic. The hair loses its shine, splits and becomes frizzy, and the nails become brittle.
A well-balanced diet should provide adequate amounts of omega-3 fatty acids, but this is not always possible. The solution is high-quality dietary supplements, which allow you to meet the body's daily requirement for omega-3 fatty acids. Their regular intake contributes to the proper functioning of the human body. This is an important preventive measure in many diseases of the nervous, circulatory or immune systems.
What should omega-3 supplementation look like?
By taking EPA and DHA supplements daily, you are not at risk of omega acid deficiency. You can do this in many ways. Omega-3 acids are available in various forms. Capsules and liquids are popular. They are often enriched with various vitamins and minerals that support the functioning of the body even better. You can also add healthy omega-3 fatty acids to your meals in the form of oil.
This may be useful to you: Ultra - vitamins and minerals for daily supplementation
Omega-3 supplementation is especially recommended for seniors, children, pregnant women, and people who do not eat oily sea fish or walnuts, vegetable oils, or seafood. The omega-3 dose depends mainly on age.
- Adults: 250 mg of omega-3 acids/day,
- Pregnant women: ALA 0.5% of dietary energy (% E), DHA + EPA 250 mg/day + 100–200 mg DHA/day,
- Breastfeeding women: ALA 0.5% of dietary energy (% E), DHA + EPA 250 mg/day + 100–200 mg DHA/day,
- Infants: ALA 0.5% of dietary energy (% E), DHA 100 mg/day,
- Children 1-2 years: ALA 0.5% of dietary energy (% E), DHA 100 mg/day,
- People 2-18 years old: 250 mg of omega-3 fatty acids/day.
Supplementation should also ensure an optimal ratio of omega-3 to omega-6 acids.